Higher Education: Qualifications Explained
Here is a guide to explain the different levels of courses available.
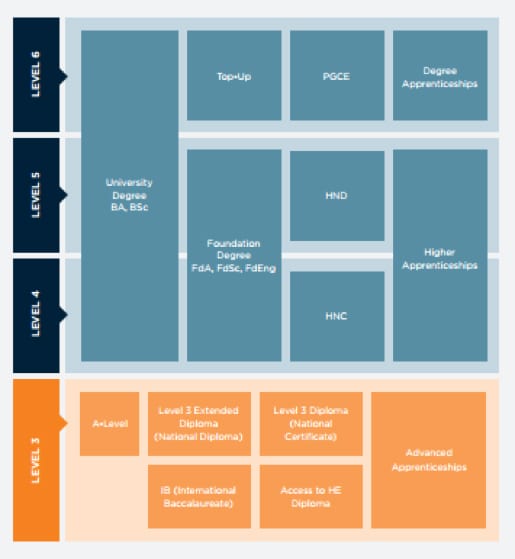
Higher National Certificate (HNC):
Level 4 vocational qualifications that usually take one year to complete, and provide practical knowledge and skills in a specific industry or sector. Successful completion can lead to employment, career progression, HND or second year of an honours degree (dependent on subject studied and HE providers’ entry requirements).
Higher National Diploma (HND):
Level 5 vocational qualifications that usually take two years to complete, and provide practical knowledge and skills in a specific industry or sector. A HND is equivalent to the first two years of a degree. On completion, you can either go into employment or apply to study a top-up degree (dependent on subject studied and HE providers’ entry requirements).
Foundation Degrees (FdA or FdSc):
Level 5 qualifications that combine academic study with work-based learning. They are designed in collaboration with employers and can be topped up to a full degree with further study.
Top-up Degrees (BA/BSc):
Level 6 qualifications that allow students with an HND, Foundation Degree, or equivalent to top up their qualification to a full Bachelor’s degree, usually with one additional year of study (dependent on subject studied and HE providers’ entry requirements).
Higher Technical Qualifications (HTQs):
Level 4 and 5 qualifications that have been quality marked by the Institute for Apprenticeships and Technical Education (IfATE). HTQs are designed to meet the higher technical skills needs of employers and provide a progression route into skilled employment or further study.
Higher Apprenticeships:
Work-based programmes that combine employment with part-time study at Levels 4-7. They allow students to earn a salary while gaining a nationally recognised qualification and developing job-specific skills.
If you prefer to earn as you learn, you can study university qualifications with a Higher Apprenticeship.
Lancashire and Cumbria Institute of Technology (IoT):
IoTs are collaborations between further education colleges, universities, and employers. They offer higher technical education and training in STEM subjects, focusing on delivering the technical skills employers need.
Find out more about the Lancashire and Cumbria Institute of Technology
Postgraduate Certificates (PGCE):
Level 7 qualifications that are shorter than a full Master’s degree. They provide specialised knowledge and skills in a particular subject area and can often be completed on a part-time basis. Examples include the Postgraduate Certificate in Education (PGCE) for teacher training.
Professional Qualifications:
Work-related qualifications that are designed to meet the needs of specific industries or job roles. Examples include the Association of Accounting Technicians (AAT) Level 4 Diploma for accounting professionals and the Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages (TESOL) qualification for English language teachers.
Modular Acceleration Programme (MAP):
Flexible, part-time courses that allow students to study individual modules from existing HE programmes. MAP courses are designed for adult learners who want to upskill or reskill in a particular area without committing to a full degree.
Additional Information
What qualification levels mean: England, Wales and Northern Ireland – GOV.UK (www.gov.uk)
Qualifications Frameworks (qaa.ac.uk)
UCAS | At the heart of connecting people to higher education